The developed heat because of core and copper losses should be dissipated to atmosphere continuously during operation.If the heat arises by the losses is not removed then
- The developed heat damages insulation of transformer
- The transformer should be de-rated from its maximum to reduce the heat.
Since above two factors is undesirable to operate the heat from the transformer should be removed effectively.
Transformer cooling methods
1) Dry type transformers:
a) Self-air cooled Transformer(up to 3 MVA):
The transformed is allowed to cool natural conventional air flow surrounding it through heat radiation.
b) Forced Air Cooled Transformer (Up to 15 MVA):
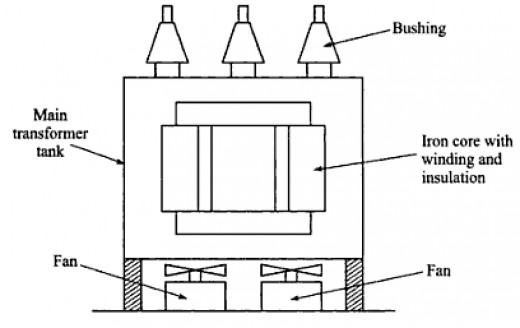
The air is circulated through the winding of transformer by means of blower. This arrangement is housed in metal box with proper insulation between windings. The blowers will blow the air through the windings and hence hot air is gained cooled by the outside natural conventional air.
2) Oil immersed type Transformer:
in this type the transformer winding and core are immersed in the mineral oil which has good electrical insulating property to block the current flow through the oil and high thermal conductivity prosperity for efficient heat removal from the windings and core.
Advantages of oil Transformer:
- Oil is a good electrical insulator
- Oil has good thermal conductivity to absorb the heat
Disadvantages of oil in Transformer
- Oil is a fire hazard and con not be used in indoor transformers.
- Oil leak in the tank or in handling leads to pollution of the environment.
- Moisture in the oil should be continuously monitored and removed which reduces the electrical insulating property of oil.
a) Oil-Immersed Self cooled Transformer:
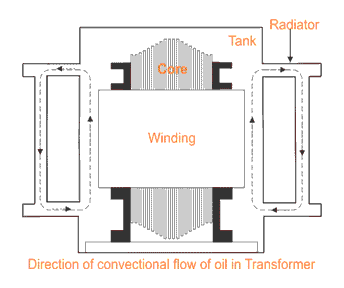
In this type the transformer windings and core are cooled by the mineral oil. The heated oil circulated through radiator by national convention and hence cooled by the surrounding air. This type is normally used for distribution type transformer with low ratings.
b) Oil-Immersed forced air cooled Transformer
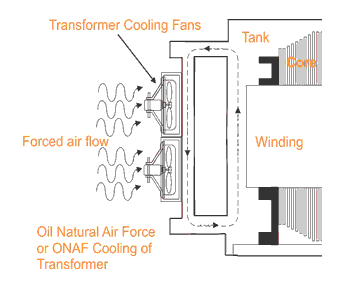
In this type the transformer is cooled by the oil which in turn cooled by the forced air in radiator. A bank of coolers or blowers is situated in the transformer radiator which forces the air through the cooling fins. The hot oil enters in these cooling fins by the natural convention and cooled oil again flows through the windings. This cooling method is used normally large transmission transformers situated outdoors, in power plants and in power stations.
c) Oil-Immersed water cooled Transformer
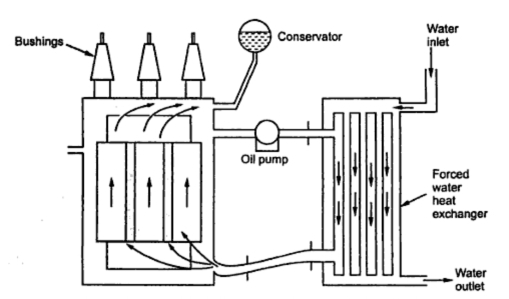
This type of cooling is used for very large transformers with very high power rating above 500 MVA. In this the Transformer is cooled by oil which then passes through the oil-water heat exchangers. Two 100 % oil pumps are placed to circulate the hot oil through the two heat exchangers. The heat oil dissipates the heat to the water and again flows through the windings and core. The service water is used for cooling. We can operate the transformer with one cooler but if two fails then we have to trip the transformer.










