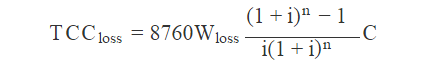Transformers reduce the voltage of the electricity supplied by the utility to a level suitable for use by the electric equipment. Since all of the electricity used by a company passes through a transformer, even a small efficiency improvement will result in significant electricity savings. High-efficiency transformers are now available that can reduce total electricity use by approximately 1 percent. Reduced electricity use provides cost savings for a company.
Two types of energy losses occur in transformers: load and no-load losses.
Load losses: result from resistance in the copper or aluminum windings. Load losses (also called winding losses) vary with the square of the electrical current (or load) flowing through the windings. At low loads (e.g. under 30 percent loading), core losses account for the majority of losses, but as the load increases, winding losses quickly dominate and account for 50 to 90 percent of transformer losses at full load. Winding losses can be reduced through improved conductor design, including proper materials selection and increases in the amount of copper conductor employed.
No-load losses: result from resistance in the transformer’s laminated steel core. These losses (also called core losses) occur whenever a transformer is energized and remain essentially constant regardless of how much electric power is flowing through it. To reduce core losses, high-efficiency transformers are designed with a better grade of core steel and with thinner core laminations than standard-efficiency models.
Total transformer losses are a combination of the core and winding losses. Unfortunately, some efforts to reduce winding losses increase core losses and vice versa. For example, increasing the amount of conductor used reduces the winding losses, but it may necessitate using a larger core, which would increase core losses. Manufacturers are developing techniques that optimize these losses based on the expected loading.
Annual energy losses and cost of these losses:
The annual energy losses of a transformer can be estimated from the following formula
Wloss = 8760(Po+Pk L2)
Where,
Wloss – is the annual energy loss in kWh.
Po – is the no-load loss in kW.
Pk – is the short-circuit loss (or load loss) in kW.
L – is the average per-unit load on the transformer.
8760 – is the number of hours in a year.
To calculate the cost of these losses, they need to be converted to the moment of purchase by assigning capital values, to be able to put them into the same perspective as the purchase price. This is called the Total Capitalized Cost of the losses, TCC loss. This can be calculated using the following formula
Where,
C – is the estimated average cost per kWh in each year.
i – is the estimated interest rate.
n – is the expected life time of the transformer.