A motor is an electro-mechanical device which converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. and a 3 phase motor runs at synchronous speed is called synchronous motor.Synchronous motor mainly runs on principle of magnetic locking between rotor and RMF(Rotating magnetic field).When two unlike poles are brought near each other, if the magnets are strong, there exists a tremendous force of attraction between those two poles. In such condition the two magnets are said to be magnetically locked.
Synchronous Motor Working Principle:-
When 3 phase voltage applied to electric conductors are placed in a certain geometrical positions which are specially arranged (In certain angle from one another) rotating magnetic field produces.this RMF rotates with synchronous speed.The synchronous speed of a stator rotating magnetic field depends on the supply frequency and the number of poles for which stator winding is wound. if the frequency of the a.c. supply is f Hz and stator is wound for P number of poles, then the speed of the rotating magnetic field is synchronous given by,
Ns = 120f/P rpm.
Synchronous Motor Working Principle
How Rotor Rotates at Synchronous Speed?
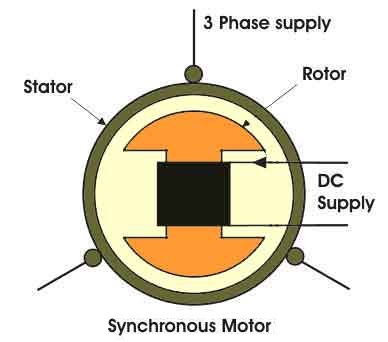
Now to understand the concept of synchronous motor working,consider a two pole simple rotor(shown in fig).Synchronous motor is a doubly excited machine i.e two electrical inputs are provided to it. It’s stator winding which consists of a 3 phase winding is provided with 3 phase supply and rotor is provided with DC supply.when DC supply given to rotor it acts like a electromagnet.as we know rotating magnetic field rotates with synchronous speed when two opposite poles of rotor and RMF locked rotor also rotates with same speed of RMF in the direction of rotating magnetic field.Hence synchronous motor rotates at one and only one speed i.e. synchronous speed. But this all depends on existence of magnetic locking between stator and rotor poles. Practically it is not possible for stator poles to pull the rotor poles from their stationary position into magnetic locking condition. this is the reason why synchronous motors are not self starting.
Methods of Starting of Synchronous Motor:-
1.Pony motor method:
Synchronous motors are mechanically coupled with another 3 phase induction motor or DC shunt motor. DC excitation to the rotor is not fed initially. It is rotated at speed very close to its synchronous speed and after that DC excitation is given to the rotor. After some time when magnetic locking takes place supply to the external motor is cut off from coupling.
2.Damper winding Method:
In damper winding method synchronous motor is first run as three phase induction motor using damper winding and finally it is synchronized with the RMF.
Application Of Synchronous Motors
1.It is used where high power at constant speed is required.EX: rolling mills, chippers, mixers, pumps, pumps, compressor etc.
2.As synchronous motor is capable of operating under either leading and lagging power factor, it can be used for power factor improvement. A synchronous motor under no-load with leading power factor is connected in power system where static capacitors can not be used.
3.Synchronous motor finds application where operating speed is less (around 500 rpm) and high power is required.











