To get a clear idea about this question consider a rotating magnetic field as equivalent to physical rotation of two stator poles N1 and S1 as shown in the figure.Assume any instant like that two poles are in line with stator magnetic axis [A-B].At this instant, rotor poles are arbitrarily positioned as shown in the below figure.
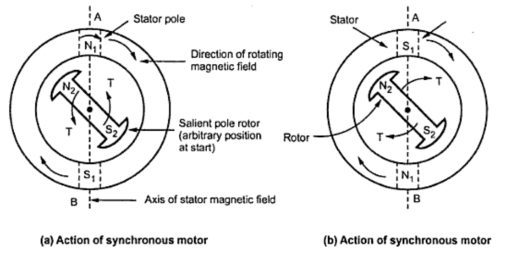
When DC supply is given to stationary rotor unlike poles will try to attract each other.Because of this action rotor will be subjected to an instantaneous torque in anticlockwise direction.As we connected power supply to stator,stator poles will rotate at speed of Ns r.p.m.
Due to inertia of rotor it is unable to rotate in the direction of anticlockwise torque, to which is driving force or stator rotating field.Just in that instant the stator poles change their positions. Consider an instant half a period latter where stator poles are exactly reversed but due to inertia rotor is unable to rotate from its initial position.Shown in figure (b).
At this instant, due to the unlike poles trying to attract each other, the rotor will be subjected to a torque in clockwise direction. This will tend to rotate rotor in the direction of rotating magnetic field.But before this happen, stator poles again change their position reversing the direction of the torque exerted on the rotor.
Hence the average torque on the rotor is zero.So synchronous motor will not start it self .













