What are the key differences between AC and DC motors?
As with the different types of DC motors, the main difference between AC and DC motors centers around how the magnetic fields are generated. The rotor of a typical AC induction motor has no electrical connection. The rotor is influenced by the field generated by the stator, which is fed an AC voltage. A typical DC motor has a rotor with electrical connections through a brush and commutator arrangement. The brush/ commutator acts as a switch which applies voltage to the different segments of the rotor. The field can also have either an electrical connection or can be composed of permanent magnets.
Why choose AC over DC?
AC motors and control have taken over many applications formerly driven by DC motors. One of the main reasons many people prefer AC to DC is that AC motors require less maintenance. While most motors require minimal maintenance, DC motors require an extra step of monitoring and replacing the internal brushes. While this step may be simple to perform on small motors, care must be taken on higher horsepower DC motors to correctly install motor brushes. On smaller (2HP or less) Permanent Magnet motors, the brush change-out can be accomplished in a matter of minutes.
Why choose DC over AC?
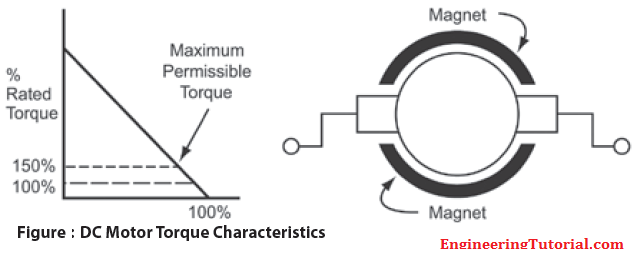
There are several reasons to choose DC motors over AC motors. High performance (especially at low speeds), high power density, simplicity of control, and a large installed base help determine applications for DC motors. DC motors develop full-load torque at low speeds (Below Figure). This, combined with low inertias, result in excellent performance from DC motors. AC motors and controls have closed the performance gap, but general purpose DC motors still outperform general purpose AC motors. To obtain comparable low-speed performance from an AC motor, much more expensive AC drives and motors must be used.
DC motors generally have much higher power density than AC motors. This allows a customer to use a physically smaller DC motor than the equivalent-HP AC motor. The control system for a DC motor is much simpler and less expensive than an equivalent AC drive.
An AC drive must rectify incoming AC power into a DC bus and then create its own AC voltage to send out to the motor. A DC drive rectifies the incoming AC waveform and passes that rectified power out to the DC motor.
While AC motors and controls have made large inroads, DC motors have been around for 100 years and have been used extensively in almost all industrial applications. There is a large installed base of DC motors in the automation industry. Usually, replacing an existing DC motor with a new DC motor is much quicker, easier and economical than redesigning a control system to incorporate an AC motor and drive.
How do you power DC motors?
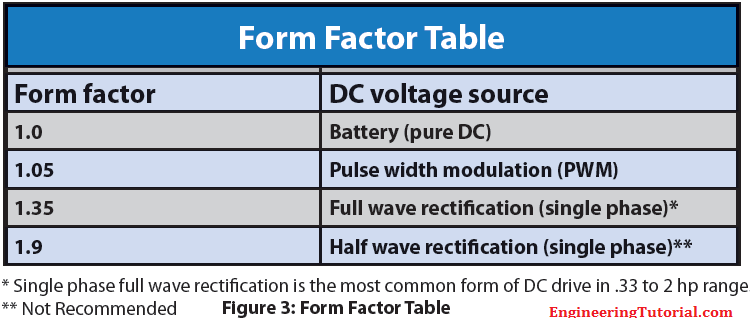
DC motors can be fed from a variety of DC power sources, even batteries. Typically, though, industrial DC motors are driven from DC drives. The quality of output power from different types of DC drives varies dramatically. This quality can be measured by how much ripple current is produced by the drive. The ripple current is designated by a drive’s Form Factor, which is the relationship of the ripple current to the main DC current. High ripple current results in increased motor heating and possibly premature brush failure.
A battery is considered the ideal current source, which has a current Form Factor of 1.0. With a battery, there is a constant voltage (and current) to power the motor. A Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) DC drive emulates pure DC so well, that it generally produces a Form Factor of 1.05 (only 5% ripple) (Shown in Below Figure).
One of the more common drives for small horsepower DC motors is the Single-Phase Full-Wave Rectified DC Drive. This drive takes an AC voltage and passes the positive half of the wave and rectifies the negative part of the wave to produce a waveform with a Form Factor of 1.4 (40% current ripple). These drives are commonly referred to as SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) drives. Many motors are “SCR-rated”, meaning their full load torque and power are produced when using an SCR drive.
Another type of drive has a much worse Form Factor: Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectified DC drives. These drives only pass the positive half of the AC sine wave. These drives have a form factor of 1.9 and are not recommended for use with many DC motors.
What is the maintenance for a DC motor?
DC motor maintenance follows basic AC motor maintenance standards (keep the motor and fan clean, grease the bearings if non-sealed, etc). DC motors have one extra step: brush maintenance. A general rule of thumb is to replace the brushes once they reach 1/3 of their original length. A good rule of thumb is to replace the brushes every 2,500 hours of use. This will ensure that the brushes are always within spec.