In the previous article we came to know that synchronous motors are not self starting so to make them start automatically we should add some tweaks.We should rotate rotor near to the speed of synchronous speed,so it attains synchronous speed.We have some fine methods to start the synchronous motor.
They are,
1. Using pony motors.
2. Using small d.c. motor.
3. As a slip ring induction motor.
4. Using damper winding.
1. Pony Motor Method / Induction Motor
Pony motors are small motors mostly induction motors,which are used to run the rotor near to the synchronous speed. Once the rotor attains the synchronous speed, the d.c. excitation to the rotor is switched on.Pony motors are connected to the shaft of synchronous motor only up to it attains synchronous speed.Once the synchronism is established pony motor is decoupled. The motor then continues to rotate as synchronous motor.
In the below figure we tried to show you pony motor connection to synchronous motor.This is not exact arrangement what we use in industries.
2. Using Small D.C. Machine
This is also similar to pony motor method with some advantages.Mostly this method employed for large synchronous motors.For synchronous motor a dc machine will be connected.This dc machine is used as a d.c. motor to rotate the synchronous motor at a synchronous speed.. Once motor starts running as a synchronous motor, the same d.c. machine acts as a d.c. generator to supply dc to the rotor of syn. motor.This have some advantages like low power usage and easy starting.
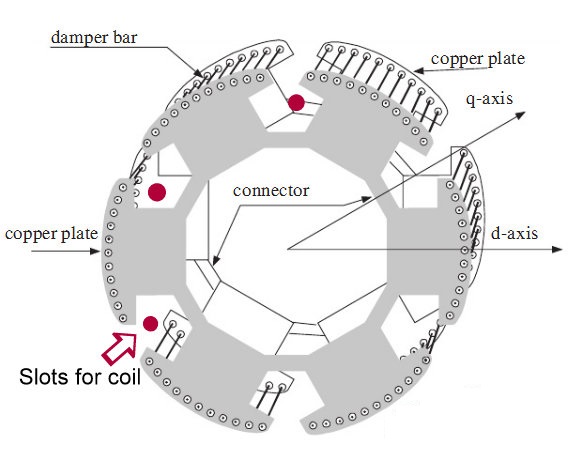
3.Using Damper Winding
This is the most used method of starting synchronous motor.In addition to the normal field winding an additional winding consisting of copper bars placed in the slots in the pole faces.Ends of the copper bars are short circuited with the help of end rings.This winding is called damper winding.This damper winding acts as a squirrel cage rotor of an induction motor.
First synchronous motor runs as induction motor due to the damper winding at sub synchronous speed.Then d.c. supply is given to the field winding. At some instant motor gets pulled into synchronism and starts rotating at a synchronous speed.As rotor rotates at synchronous speed, the relative motion between damper winding and the rotating magnetic field is zero. Hence when motor is running as synchronous motor, there can not be any induced e.m.f. in the damper winding. So damper winding is active only at start, to run the motor as an induction motor at start.
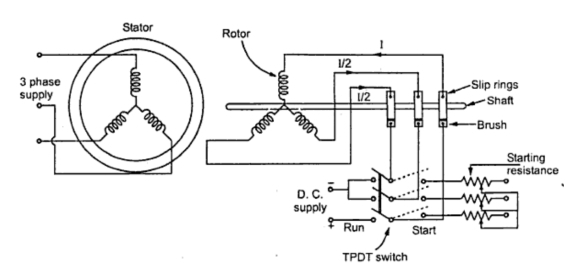
4. Slip Ring Induction Motor
In this method an external rheostat then can be introduced in series with the rotor circuit. So when stator is excited, the motor starts as a slip ring induction motor and due to resistance added in the rotor provides high starting torque.
The resistance is then gradually cut off, as motor gathers speed. When motor attains speed near synchronous. d.c. excitation is provided to the rotor, then motors gets pulled into synchronism and starts rotating at synchronous speed. The damper winding is shorted by shorting the slip rings. The initial resistance added in the rotor not only provides high starting torque but also limits high inrush of starting current. Hence it acts as a motor resistance starter.
Also Read: Synchronous Motor Working Principle













it is well explained
Very Easy To Understand Thanks .
I have a question about the pony motor method starting a synchronous motor